A blockchain is actually a database because it is a digital ledger that stores information in data structures called blocks However, while a blockchain is a database, a database is not a blockchain They are not interchangeable in a sense thatExecutive view A blockchain is a shared decentralized ledger, enabling business disintermediation and trustless interactions, thereby lowering transaction costs 2 The IT architect and data management view A blockchain is a shared appendonly distributed database with full replication and a cryptographic transaction permissioning model 3 · Blockchain data structure The blockchain data structure is an ordered, backlinked list of blocks of transactions The blockchain can be stored as a flat file, or in a simple database The Bitcoin Core client stores the blockchain metadata using Google's LevelDB database Blocks are linked "back," each referring to the previous block in the chain
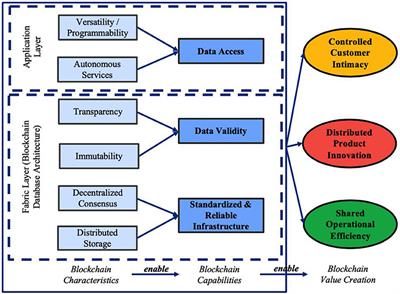
Frontiers Value Creation From A Decentralized Car Ledger Blockchain
Blockchain database structure
Blockchain database structure-13 Blockchain as a database structure 131 Data storage and management 132 Blockchain database structure and decentralization 21 133 Comparing attributes of traditional blockchain, distributed and decentralized databases 22 14 Permissioned and permissionless blockchains 23 15 Consensus methods 25 151 ProofofWork (PoW) 25 · Build new database technologies that integrate blockchain concepts, but which can still provide economic performance Create an integration layer between databases and existing blockchains There have been some early attempts to build new database systems that are based on blockchain foundations Unfortunately, rather than being "best of both




Blockchain Nist
A blockchain is a database or a ledger that stores information in a data structure called blocks It is based on distributed ledger technology which can be used between parties that don't trust each other with data It is because when you add anything onto the blockchain, it requires verification from all other users available on the network1604 · Blockchain vs Database Comparison Blockchain vs Database Architecture Considering the architecture, both blockchain and database structure are much different Blockchain uses a distributed ledger network architecture It is a peertopeer enabled network Each peer connects with another using secure cryptographic protocols · The blockchain is a chain of blocks which conta i n specific information (database), but in a secure and genuine way that is grouped together in a network (peertopeer) In other words, blockchain is a combination of computers linked to each other instead of a central server, meaning that the whole network is decentralized
Database System Concepts 7th Edition 266 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan Blockchain Properties and Structure Node types • Full node – maintains copy of blockchain and participates in the consensus process • Light node – submits updates to the blockchain but does not participate in the consensus process Consensus algorithms to choose node to add next block0506 · You can define data structures within the smart contracts, essentially turning the blockchain into a database You can build a permissions capability into smart contracts – essentially baking your security model into the blockchain itself in a way that cannot be modified without majority consensus You can define workflow for a number ofBlockchain Data Structure/ Merkle Tree 23 Bl o c k c h a i n T e c h n o l o g y S ta c k 2 5 Shared Data 26 Protocols 26 Although many people like to understand blockchain as a database, It is much more than a database It is a combination of distributed or shared databases with public or
Despite its apparent complexity, a blockchain is just another type of database for recording transactions – one that is copied to all of the computers in a participating network A blockchain is thus sometimes referred to as a 'distributed ledger' Data in a blockchain is stored in fixed structures called 'blocks' · Using the same cryptographic patterns seen in blockchain technology, each transaction is cryptographically hashed and inserted in a blockchain data structure The computed hashes of your database are then stored outside of Azure SQL Database in tamperproof storage (such as Azure immutable Blob storage , or Azure Confidential Ledger ), as database digests · Unlike traditional databases, Blockchain which was introduced in 09 by Satoshi Nakamoto is a peertopeer decentralized distributed ledger consisting of multiple nodes with replicated data that cannot be changed It is an appendonly database that is




The Difference Between Blockchain And Distributed Ledger Technology
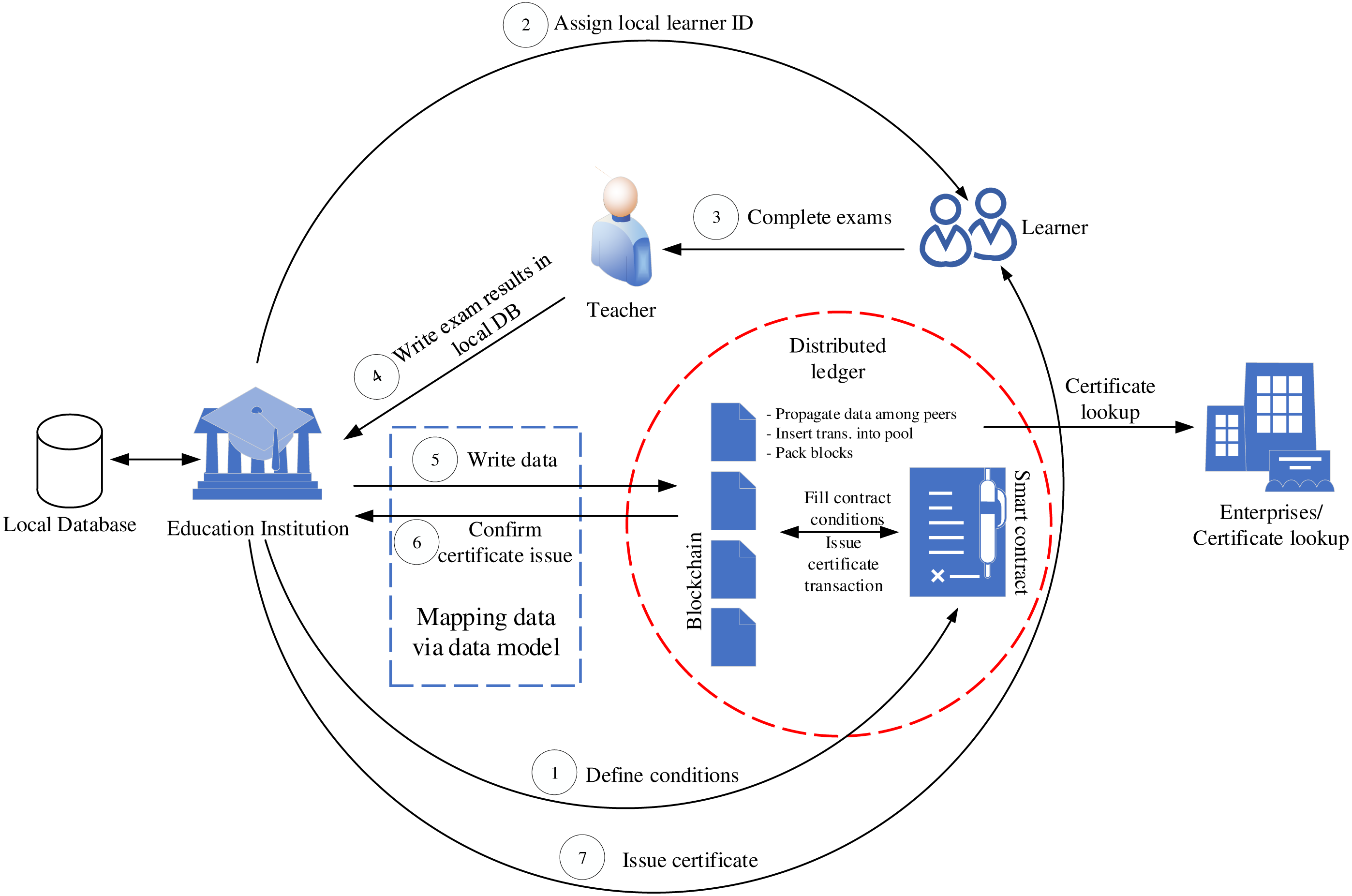



Towards A Blockchain Based Certificate Authentication System In Vietnam Peerj
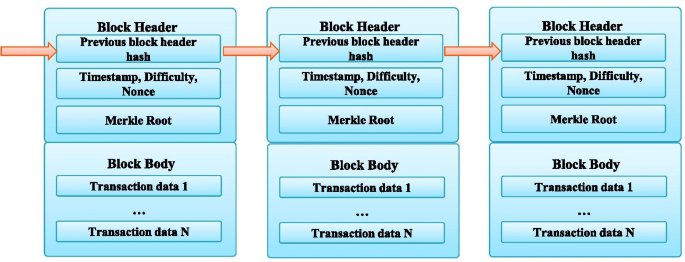
· The discussion around the blockchain and traditional databases has been active for a long time The main question is which of the two different systems is better?The blockchain in itself is a data structure that stores transactions It is similar to a linked list in that the data is split into containers the blocks Each block is connected with its predecessor with a cryptographically secured reference This makes the data structure tamperevident, changes to old blocks are easy to detect and dismissed · Broadly speaking, blockchain data structure can be described as a back linked list of transaction, arranged in blocks They can be stored in simple databases or in the form of flat files Each block is identified with the help of hash in the block header




Health Care Blockchain And Innovative Uses Freed Associates



1 Minimal Working Blockchain
Ing blockchain storage and count on trusted database servers for query integrity assurance In contrast, our proposed vChain solution builds authenticated data structures into the blockchain structure, so that even untrusted servers can queries over blockchain databases · Its appendonly structure only allows data to be added to the database altering or deleting previously entered data on earlier blocks is impossible Blockchain technology is therefore wellsuited for recording events, managing records, · You can establish data structures inside the intelligent contracts, practically covering the blockchain into a blockchain database You can create a permissions capability into intelligent contracts – practically embedding your security model within the blockchain database structure so that it can't be changed unless approved by a consensus



The Data Structure Of The Bitcoin Blockchains Download Scientific Diagram




Sap Hana Blockchain Technical Overview Sap Blogs
· Blockchain tables provide stronger database security by protecting against user fraud where someone rewrites their history, deletes certain data, or encrypts it for ransom It can also provide identity fraud protection – the optional signing of row data with the PKI signatures based on the user's private key protects against users or admins · Blockchain is a type of database, but it is quite different from a traditional database, and one of the biggest differences is its storage structure Blockchain stores data in numerous groups termed blocks Each block has a lot of information, but the space in them is limited0412 · You might think blockchain as a database that just stores information However, the difference is immense In reality, both of them are quite different, and we'll get into that shortly in the blockchain vs relational database comparison Blockchain is, by default, immutable So, it means that no one can modify any form of data whatsoever




Blockchain Vs Traditional Database What Should Be A Startup S Choice




Top 5 Use Cases And Platforms Of Blockchain Technology
0519 · As blockchain is a ledger that stores information in blocks, it actually makes it a database A database in the same way stores information in data structures named tables Nevertheless, a blockchain is a database, but a database is not a blockchain Both these structures should never be interchanged as both of them serve a different purposeA distributed database is also a decentralised data structure which features quick query processing and welldesigned data formatting but suffers from data reliability In this work, we showcase ChainSQL, an opensource system developed by integrating the blockchain with the database, ie we present a blockchain database application platformOne way to define a blockchain is a distributed database (DB) that solves the "Strong Byzantine Generals" (SBG) problem, the name given to a combination of the Byzan tine Generals Problem and the Sybil Attack Problem




How Does Blockchain Work Blockchain Transaction Intellipaat
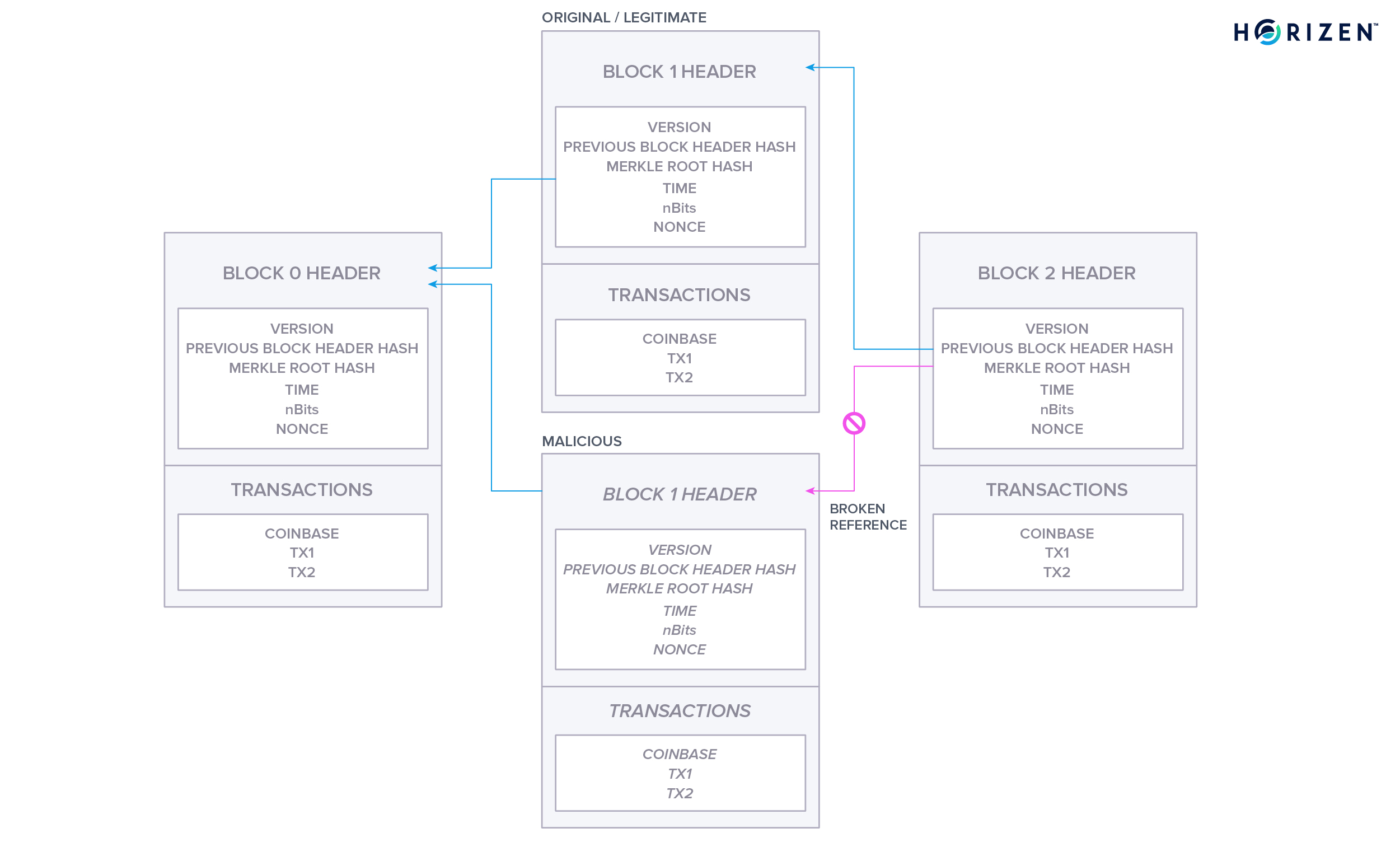



Blockchain As A Data Structure
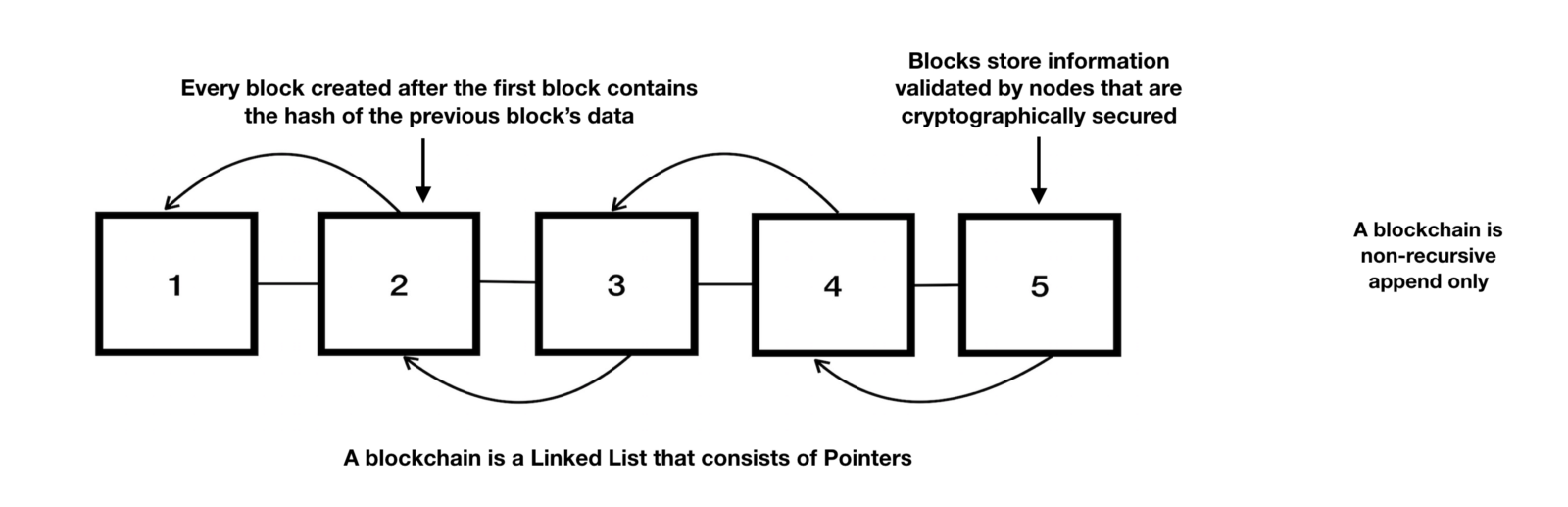
· A database structures its data into tables whereas a blockchain, like its name implies, structures its data into chunks (blocks) that are chained together · There are two data structures a blockchain holds (i) pointers and (ii) linked list Pointers are variables listing the information about the location of another variable (points out to the position of another variable) while the linked list has a sequence of blocks with each block holding specific data and links to the following blockBlockchain databases already possess a massive amount of data For example, Ethereum is estimated to have approximately 300GB of data 1 Moreover, Ethereum processed, on average, 876K transactions per day in December of 17 (Figure 1) Since the data in the blockchain cannot be deleted, the number of recorded transactions will only grow in




How To Use Blockchain To Build A Scalable Database




Blockchain Explained How Blockchain Data Is Stored And Secured Euromoney Learning
A blockchain is a data structure in the eyes of a computer scientist This structure stores information reliably, regardless of being in a trustless environment A data structure may sound technical at first, but its function is exactly that It structures your dataEvery blockchain is a distributed ledger, but not every distributed ledger is a blockchain Each of these concepts requires decentralization and consensus among nodesHowever, the blockchain organizes the · A blockchain is kind of a database because it is a digital ledger that stores information in data structures called blocks On the other hand, a traditional database is a data structure used for storing information Databases first started as flatfile hierarchical systems that provided digital storage for simple information gathering




Relational Database Schema For Blockchain Data Download Scientific Diagram




Comparison Of Traditional Database Structures And Blockchain Structures Primafelicitas
3100 · You can parse the raw database which is stored in blk*****dat files with blockchain parser and see the structure of blockchain data, so it would be the most fastest way to learn how it works – Denis Leonov Sep 1 ' at 110500 · Yes, Blockchain is a database that comes with several distinguishable traits These traits are what lead to the debate of Blockchains versus traditional databases Therefore, in this post, we would systematically approach the definitions, similarities, and differences between the two to enable a better understanding of the subject for entrepreneurs and startups looking to explore blockchain · Data structures and the blockchain The blockchain exists within a spectrum of datastructures To make the guide whole, we will first explain what different types of database types exist, what are the most common services available for each, and, finally, we will explain how organizations usually choose between each type of datastructure
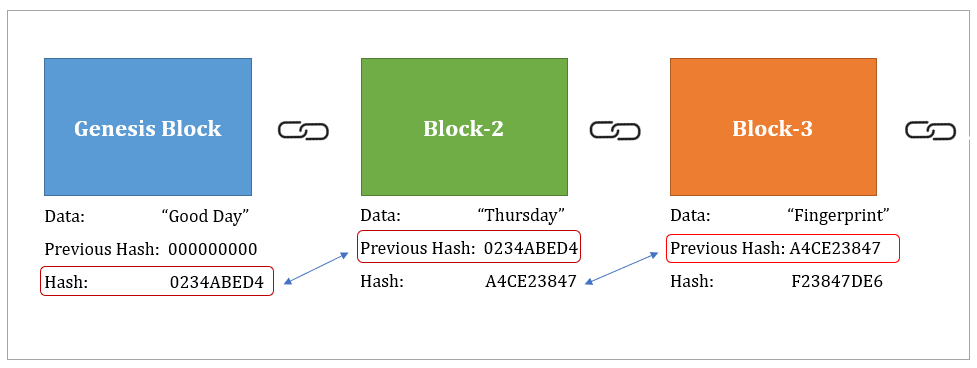



Blockchain Key Characteristics And The Conditions To Use It As A Solution By Venkat Kasthala The Startup Medium




The Blockchain Data Structure Download Scientific Diagram
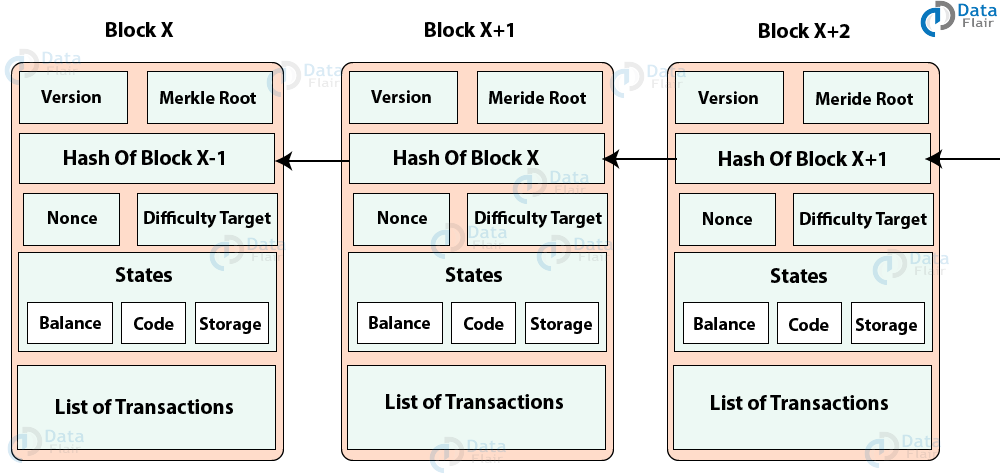
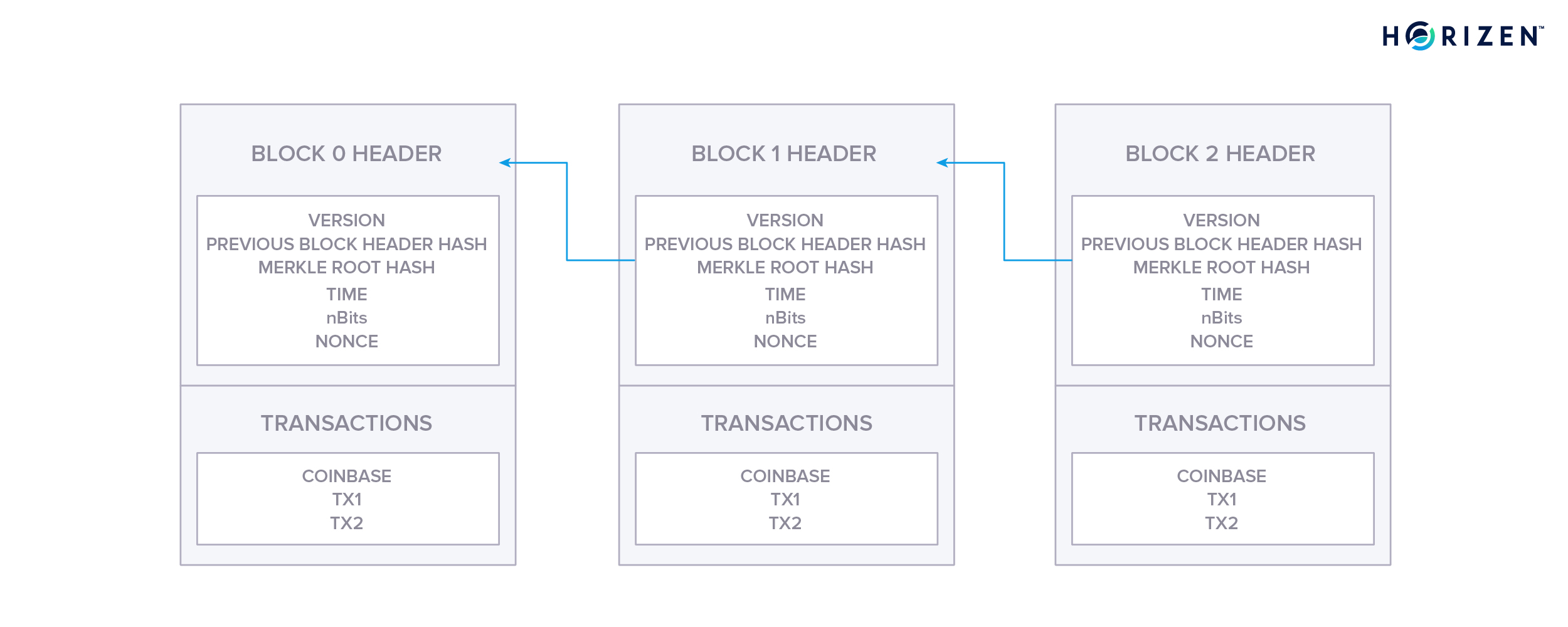
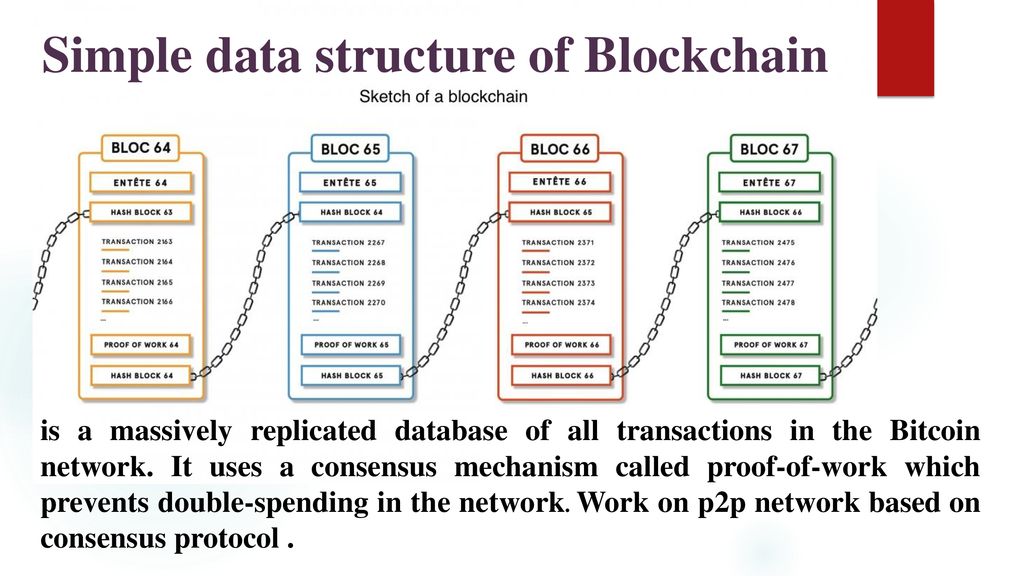
· Bitcoin blockchain structure A blockchain is a growing list of records, called blocks, that are linked together using cryptography Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data (generally represented as a Merkle tree) The timestamp proves that the transaction data existed when the block was published in order to getDatabase and Blockchain Related Paper List The repo lists recently papers of Blockchain, Outsourcing Database, Database Transaction Management, Database with modern AI and Hardware, and other related crypto tech papers0919 · Blockchain is a database structure in which a constantly growing list of records (blocks) is organized in a linear sequence where each subsequent block of information is tied to the previous block




Blockchain Nist




Blockchain Architecture Explained How It Works How To Build
The structure of the blockchain is the foundation of blockchain security Each unique transaction on the blockchain produces a unique data output known as a hash This is referred to as a transaction ID or TX ID Benefits of Blockchain There is a distinct architecture to a blockchain, with a few slight differences between various chains out there3012 · Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that enables a set of peers to work together to create a unified, decentralized network The peers can communicate and share information or data with the help of the consensus algorithm



Encrypted Blockchain Databases Part I




Blockchain Architecture Explained How It Works How To Build




Review On Blockchain Technology Based Medical Healthcare System With Privacy Issues Saha 19 Security And Privacy Wiley Online Library




Blockchain Bitcoin As A Database Newbedev




Blockchain Vs Traditional Database What Should Be A Startup S Choice




Features Of Blockchain Geeksforgeeks



Ledger Hyperledger Fabricdocs Master Documentation
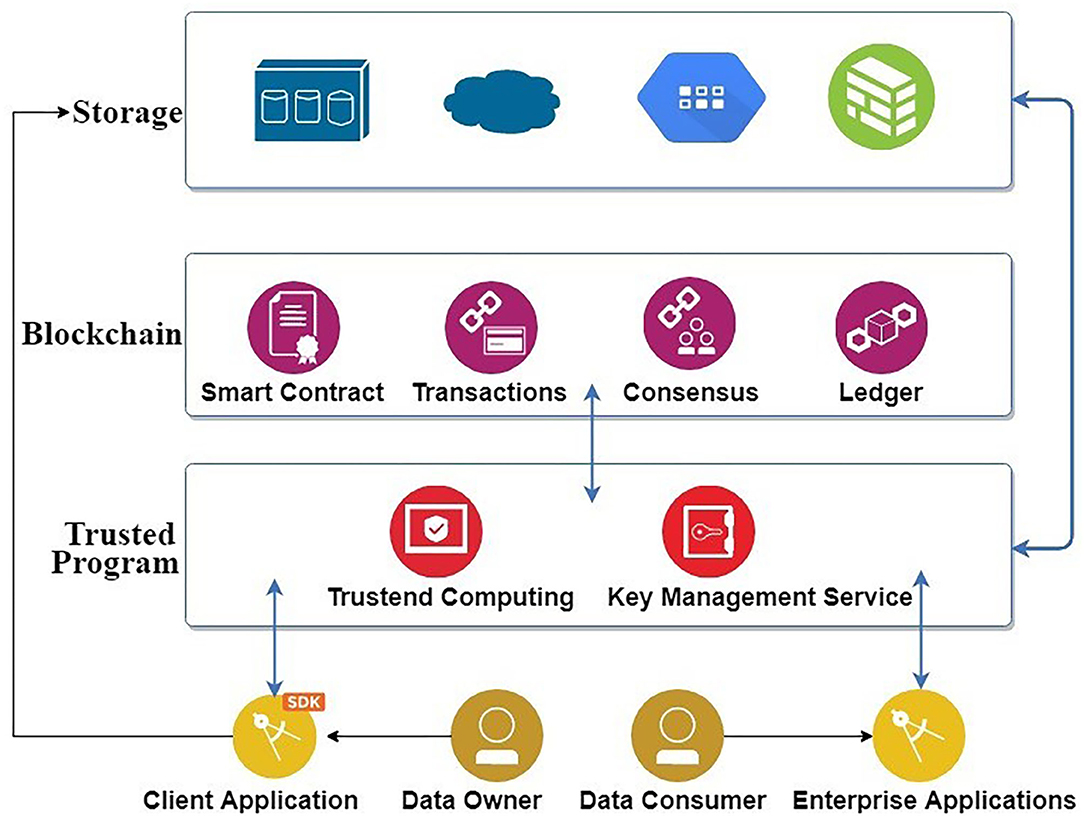



Frontiers A Blockchain Platform For User Data Sharing Ensuring User Control And Incentives Blockchain




What Is A Blockchain Data Structure Primafelicitas



How Blockchain Works Blockchain Explained Full Service Digital Marketing Agency Digital Growth Formula




Private Blockchain Vs Traditional Centralized Database Merehead
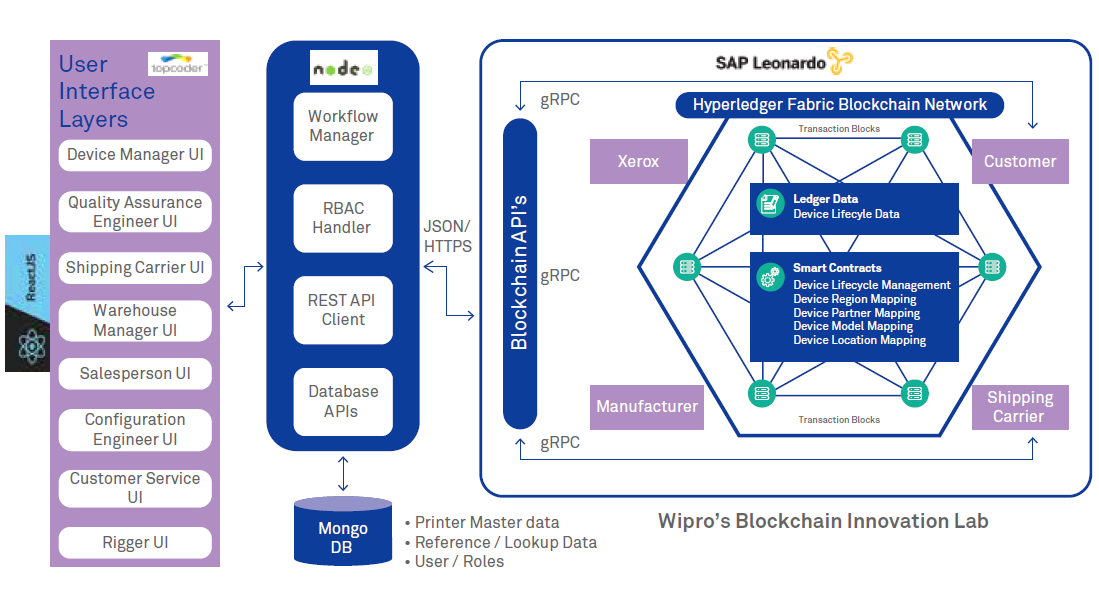



Digital Transformation In Enterprise Architecture How Is Blockchain Useful Wipro




Blockchain Data Structure And Fundamentals
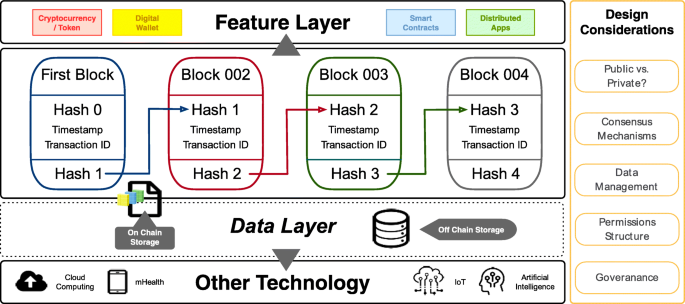



Fit For Purpose Challenges And Opportunities For Applications Of Blockchain Technology In The Future Of Healthcare Bmc Medicine Full Text
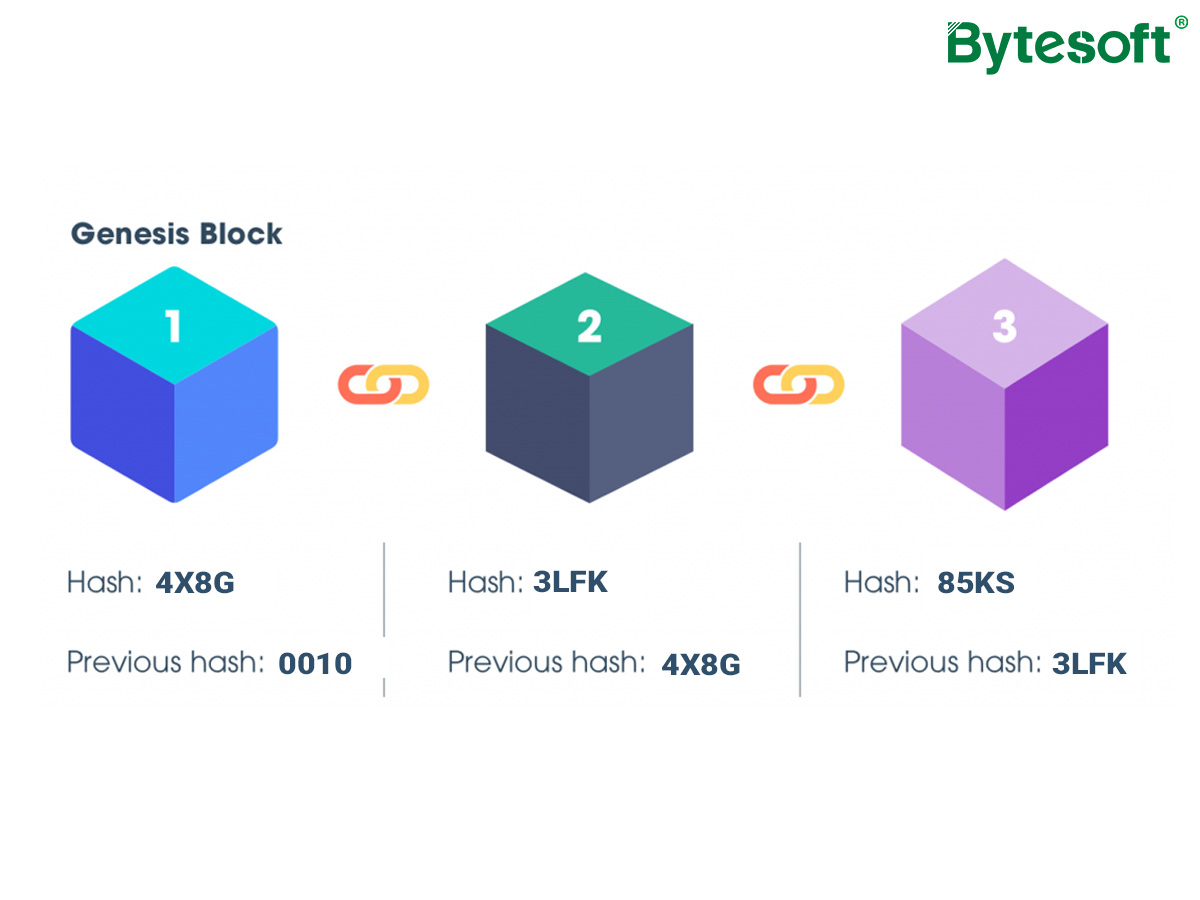



Blockchain Data Structure And How Blockchain Works




Blockchain Technology In The Energy Sector A Systematic Review Of Challenges And Opportunities Sciencedirect




What Is The Blockchain Data Structure




What Is Blockchain Database Difference Between Blockchain And Database




What Is A Merkle Tree And Why It Matters To Understand Blockchain Business Models Fourweekmba
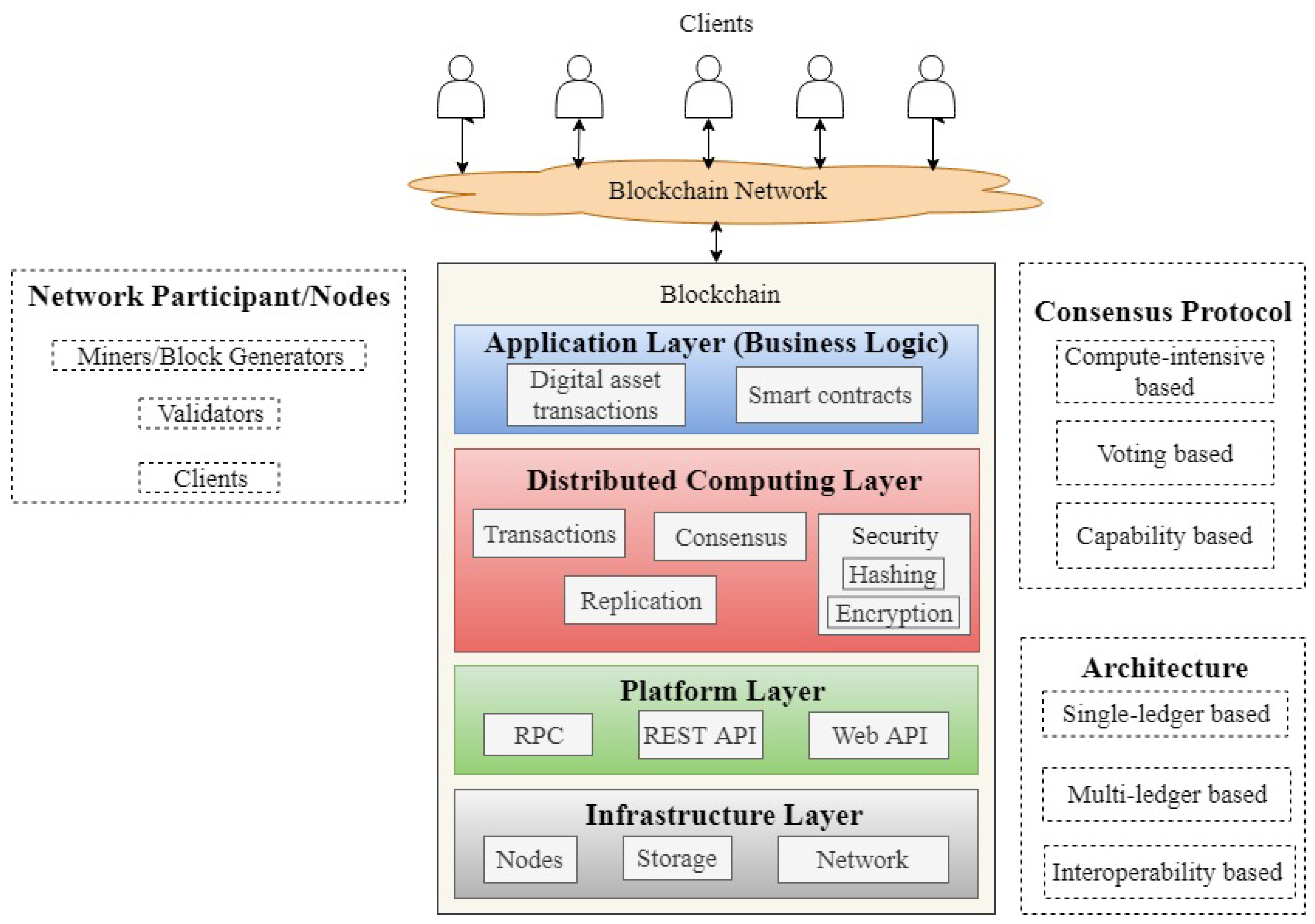



Symmetry Free Full Text A Review Of Blockchain Architecture And Consensus Protocols Use Cases Challenges And Solutions Html



Blockchain Wikipedia
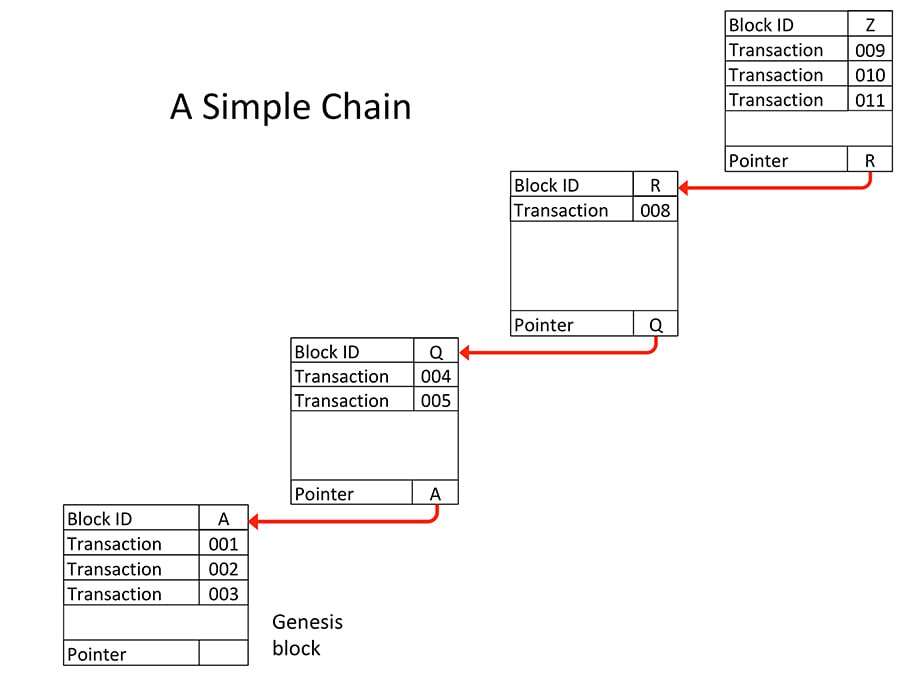



Blockchain The Facts And The Fiction s




Blockbench



Blockchain Technology Basics Spheregen
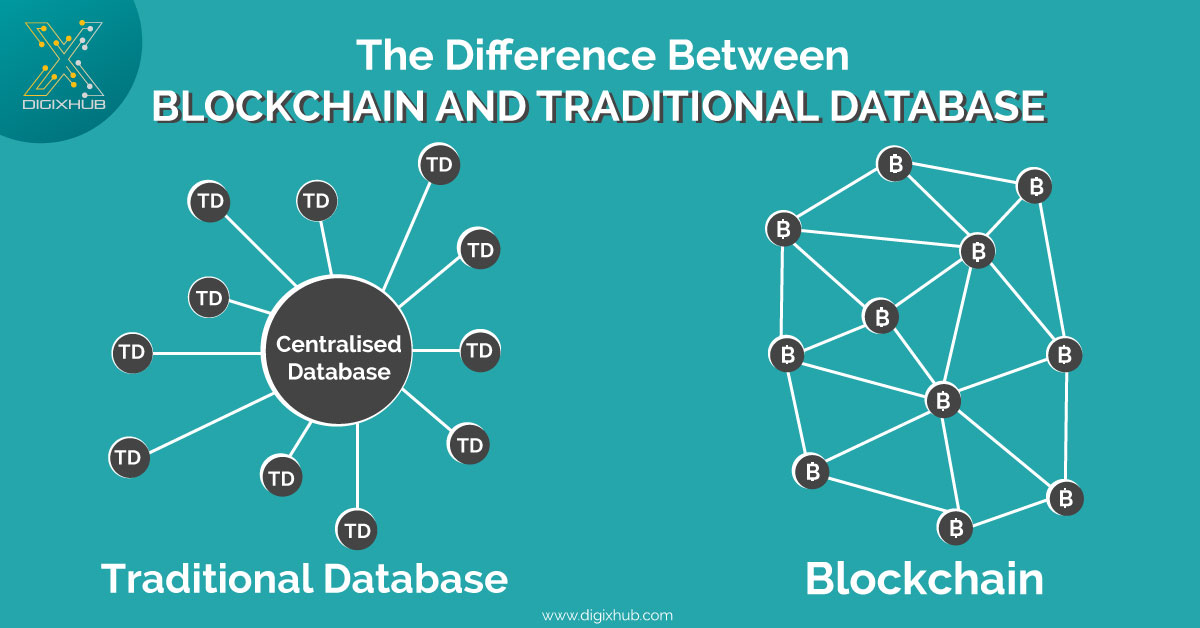



Difference Between Blockchain And Traditional Database Digixhub Blog




Blockchain Architecture Explained How It Works How To Build
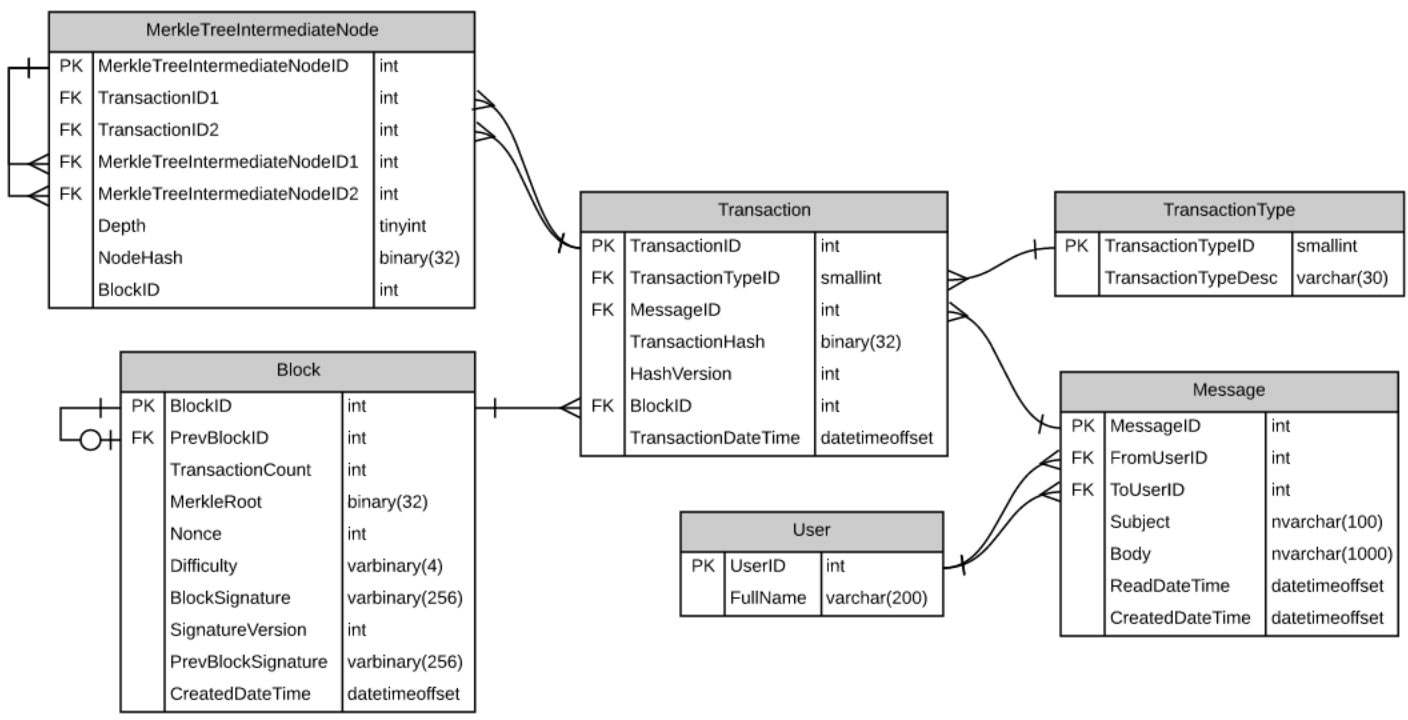



Blockchain By Example In Sql Server By Benjamin Campbell Medium
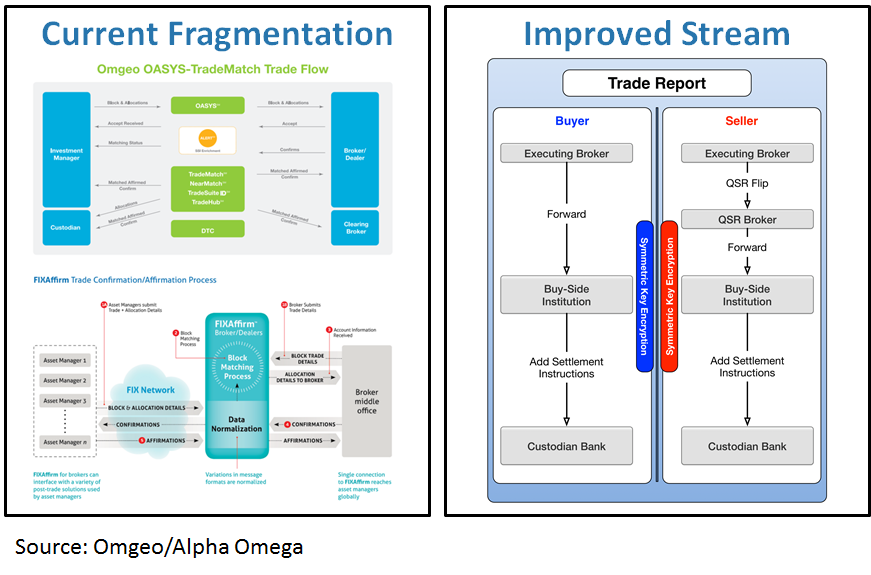



Applications And Architecture For Blockchain Style Messaging By Andy Singleton Medium




How To Import The Bitcoin Blockchain Into Neo4j




A Systematic Literature Review Of Blockchain Based Applications Current Status Classification And Open Issues Sciencedirect




Frontiers Value Creation From A Decentralized Car Ledger Blockchain




Understanding The Basics Of Blockchain Nourish The Roots Of Technology Dataflair




Eli5 Blockchain Explained In Simple Terms
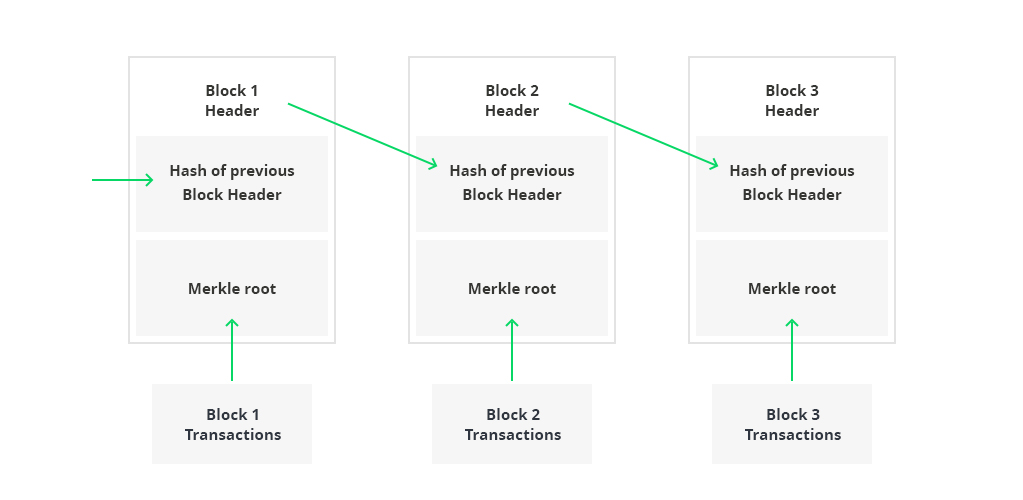



Blockchain Architecture Explained How It Works How To Build




Blockchain Vs Relational Database What S The Difference 101 Blockchains




Blockchain Architecture Download Scientific Diagram



A Survey Applications Of Blockchain In The Internet Of Vehicles Eurasip Journal On Wireless Communications And Networking Full Text



Databases And Blockchains The Difference Is In Their Purpose And Design Hacker Noon



Applications Of Blockchain Technology In The Food Industry New Food Magazine



Blockchain Architecture Simplified How It Works Edureka




How Blockchain Could Affect Manufacturing And R D F E Insights




Trust Blockchain Facilitating Online Trust Ericsson



Is Blockchain The Answer
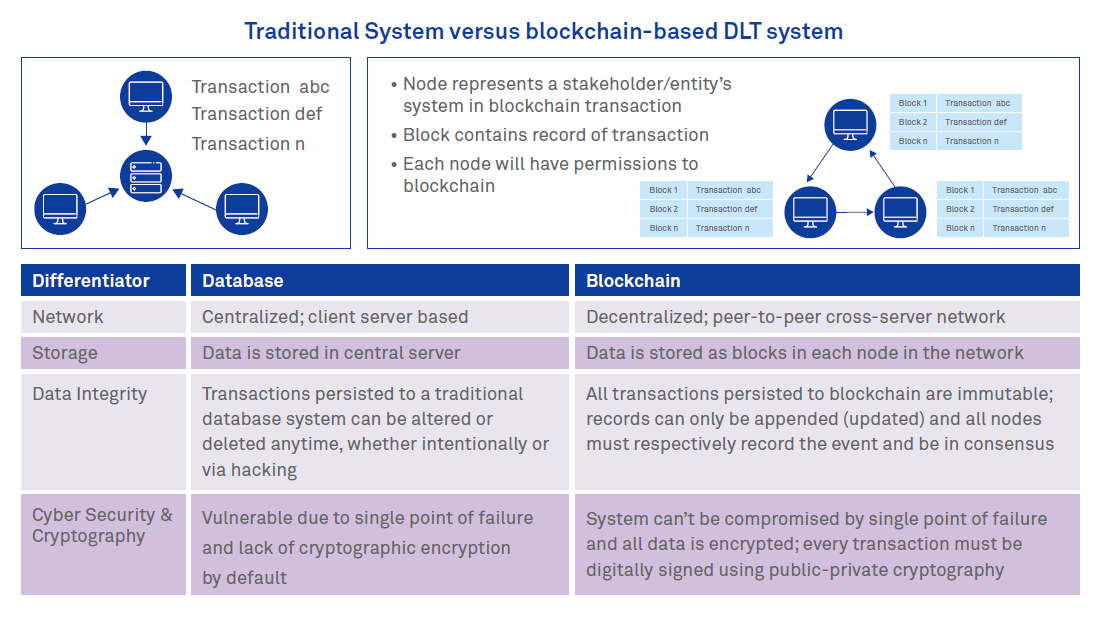



Digital Transformation In Enterprise Architecture How Is Blockchain Useful Wipro




What Is Blockchain Technology And Its Benefits For Business By Infograins Software Solutions Issuu
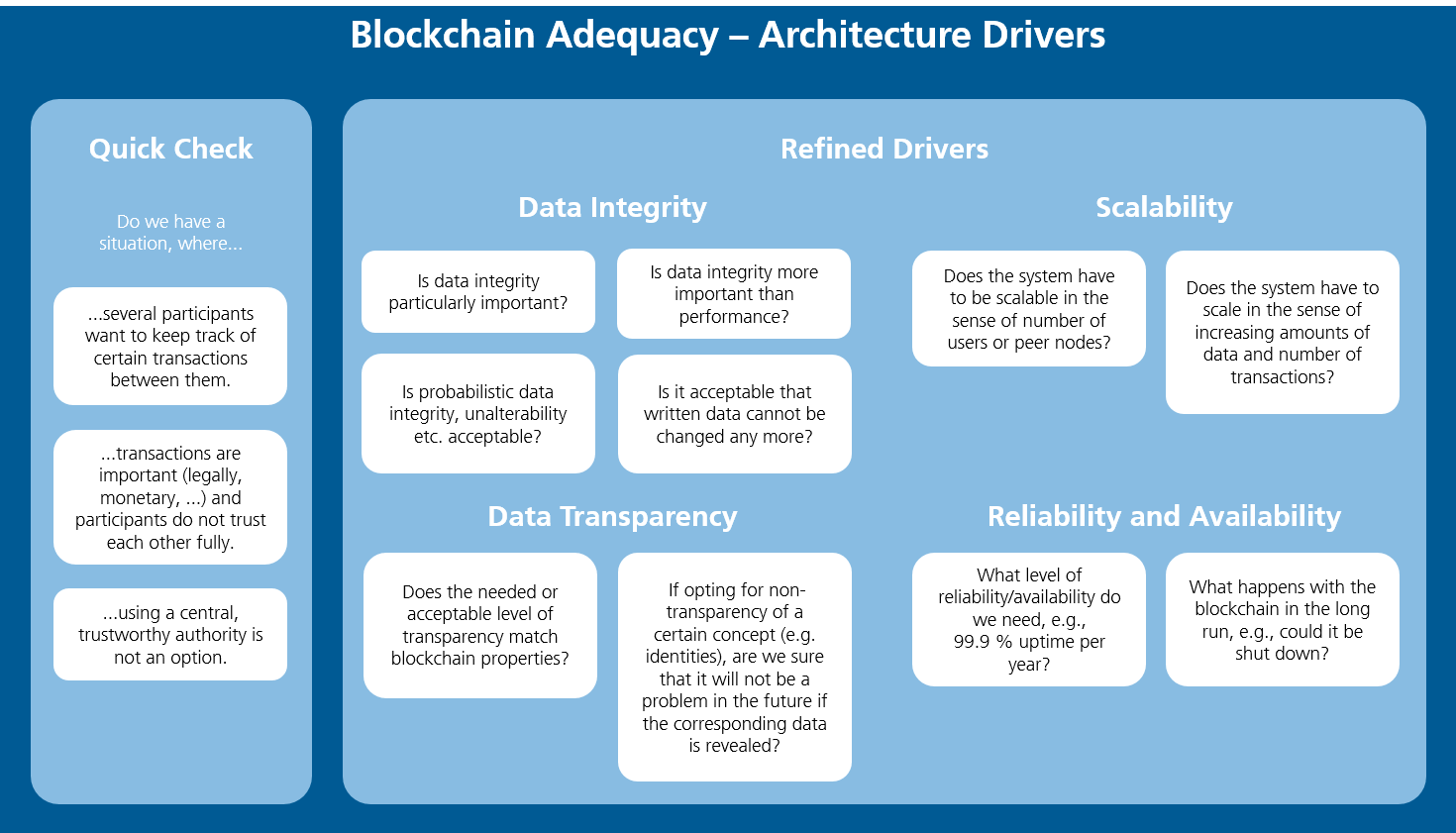



Blockchain Architecture Design Guidelines Blog Des Fraunhofer Iese




7 The Blockchain Mastering Bitcoin Book




Blockchain Vs Traditional Database What Should Be A Startup S Choice
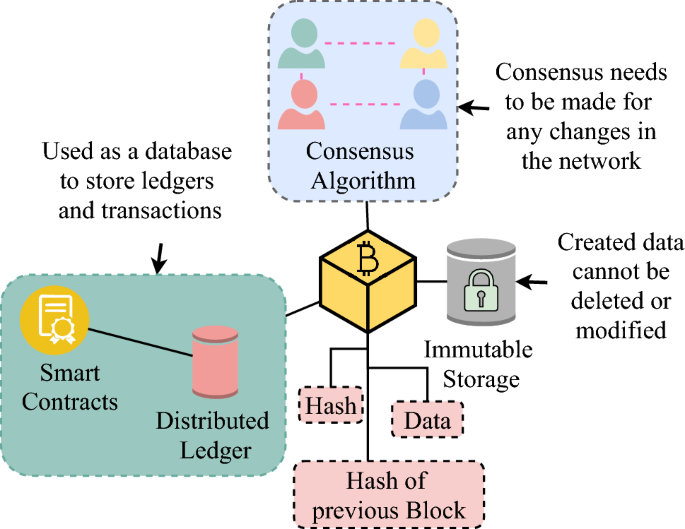



Blockchain For Decentralization Of Internet Prospects Trends And Challenges Springerlink
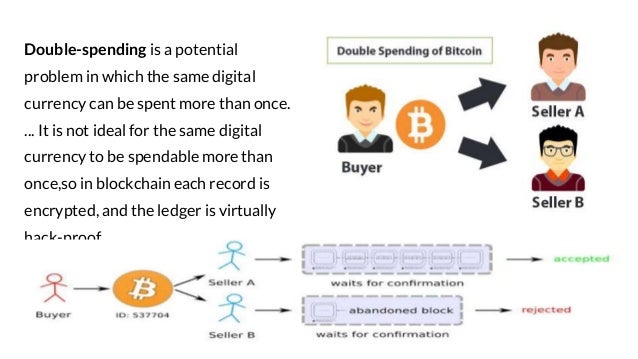



Blockchain Data Structure And Fundamentals




How To Use Blockchain To Build A Database Solution Zdnet




Blockchain Vs Traditional Database What Should Be A Startup S Choice




Message Exchange On Base Of A Blockchain Based Layered Architecture




Blockchain Wikipedia




Layered Structure Of The Blockchain Architecture Oracle Blockchain Services Quick Start Guide




Blockchain Wikipedia




Blockchain Data Structure And Fundamentals Infoclusters



Applied Sciences Free Full Text A Survey On Challenges And Progresses In Blockchain Technologies A Performance And Security Perspective Html



Understanding The Basics Of Blockchain Nourish The Roots Of Technology Dataflair




Build A Blockchain Analytic Solution With Aws Lambda Amazon Kinesis And Amazon Athena Aws Big Data Blog




A Blockchain Data Structure Download Scientific Diagram




Why Reading From Ethereum Blockchain Is Hard Anyblock Analytics




An Introduction To Blockchain Jaxenter



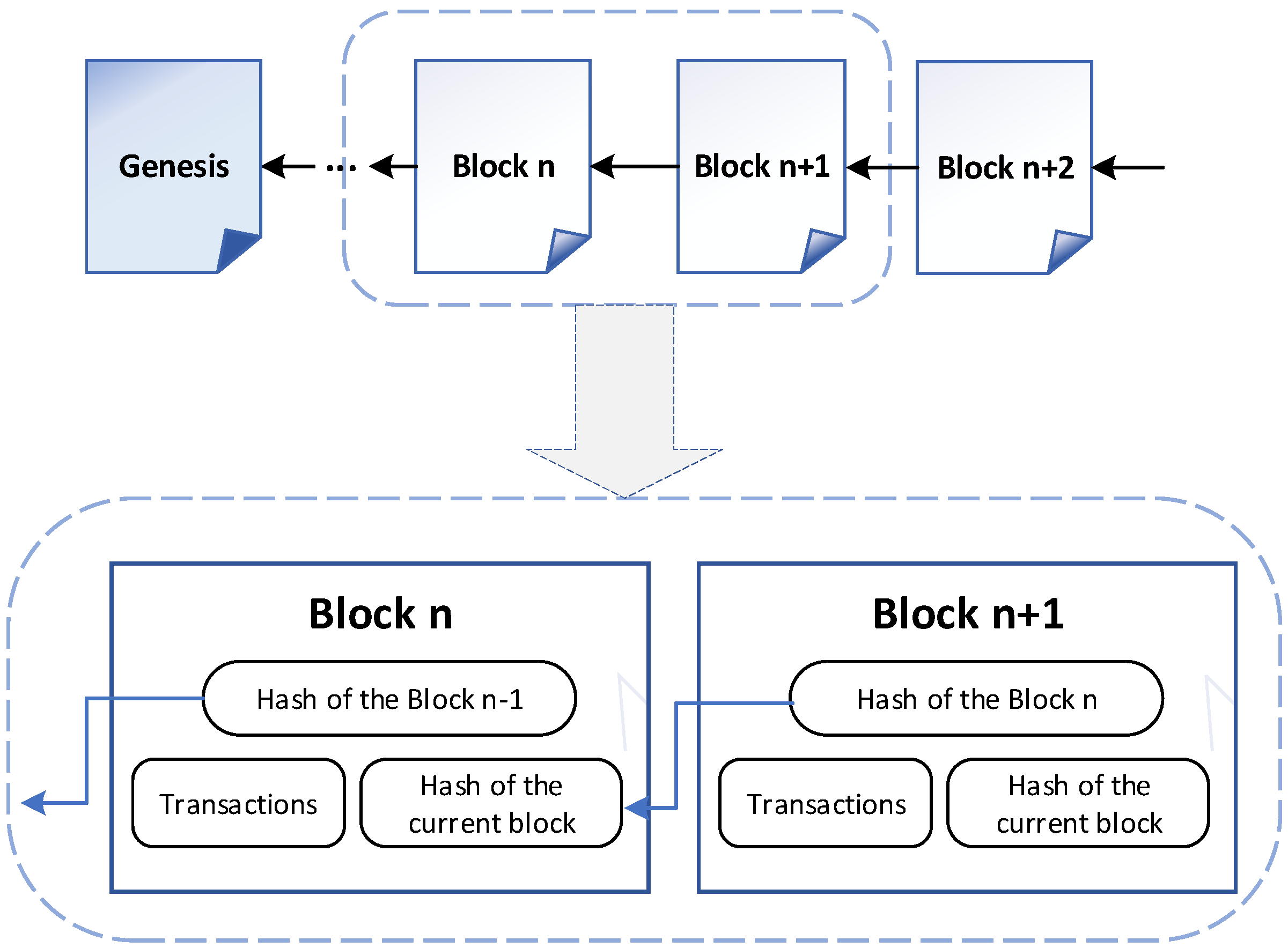
Blockchain As A Data Structure




Cryptocurrency Payment Gateway Database Schema Stack Overflow




A Survey On Security And Privacy Issues Of Blockchain Technology



Cryptocurrency And Blockchain Technology Ppt Download




Blockchain As A Data Structure
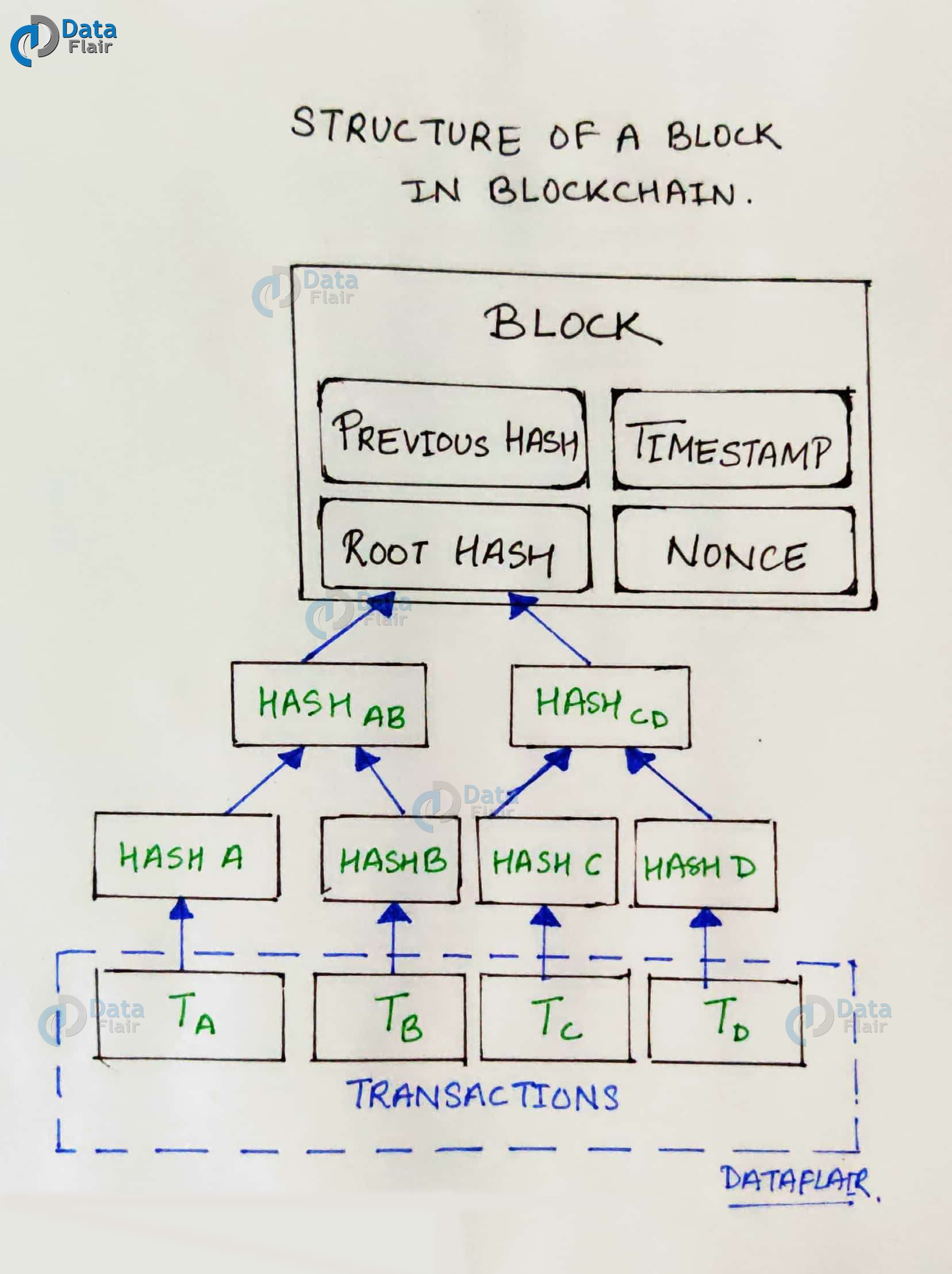



Understanding The Basics Of Blockchain Nourish The Roots Of Technology Dataflair
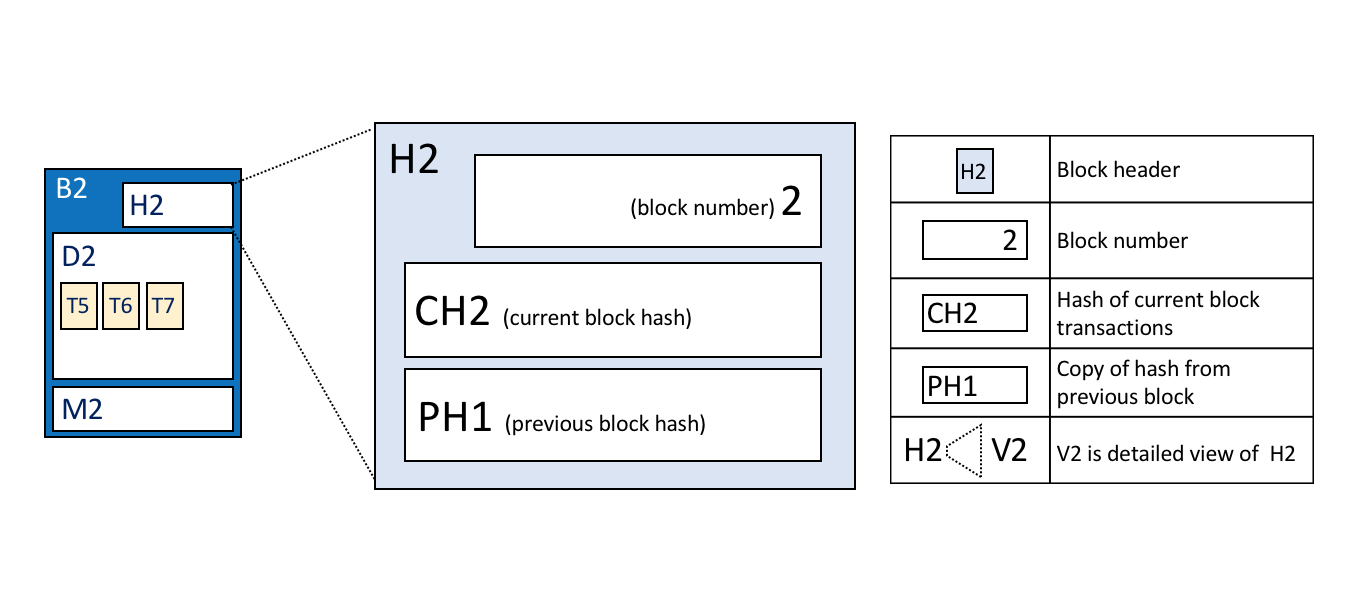



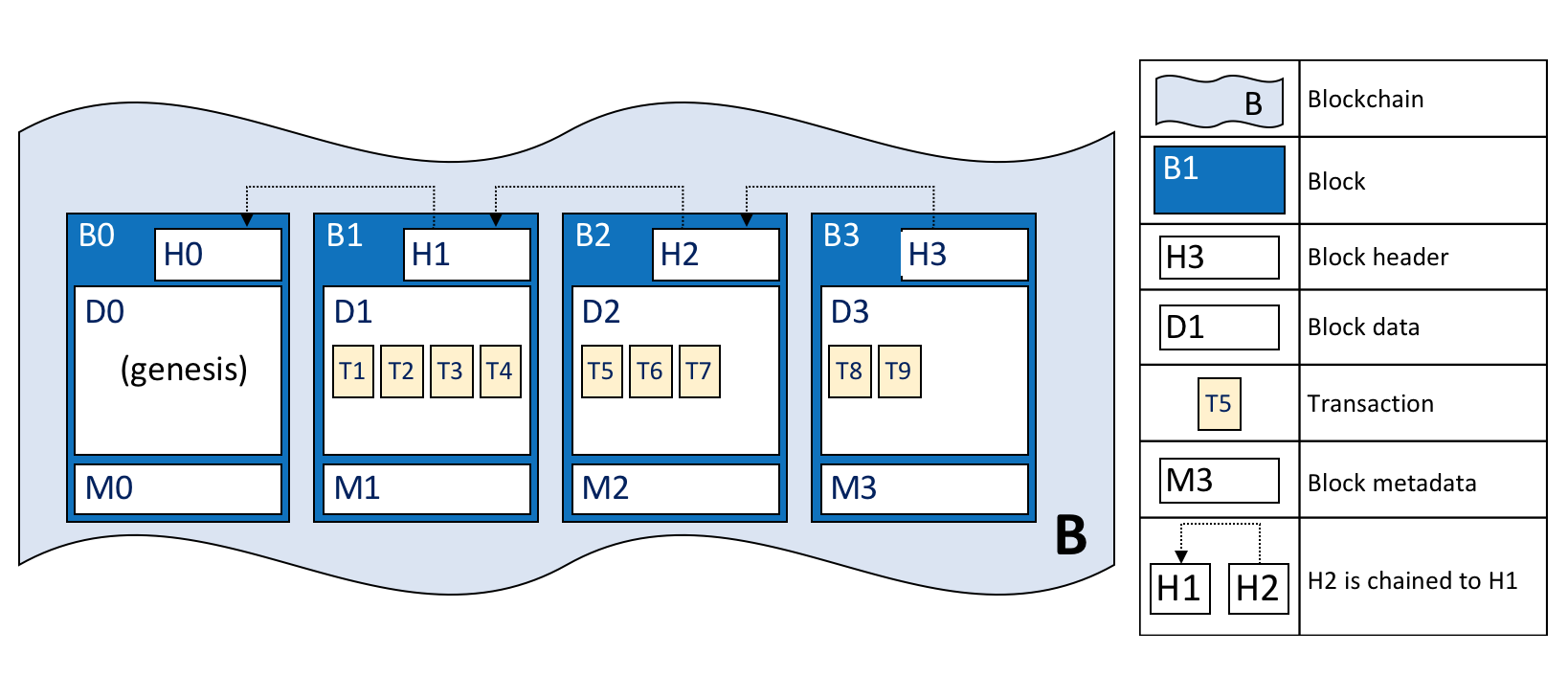
Ledger Hyperledger Fabricdocs Master Documentation
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Blockchain_Sep_2020-01-60f31a638c4944abbcfde92e1a408a30.jpg)



Blockchain Definition What You Need To Know




Untangling Blockchain A Data Processing View Of Blockchain Systems




What Is Blockchain Database Difference Between Blockchain And Database




What Is The Blockchain Data Structure



What S The Difference Between Blockchain And A Database Quora
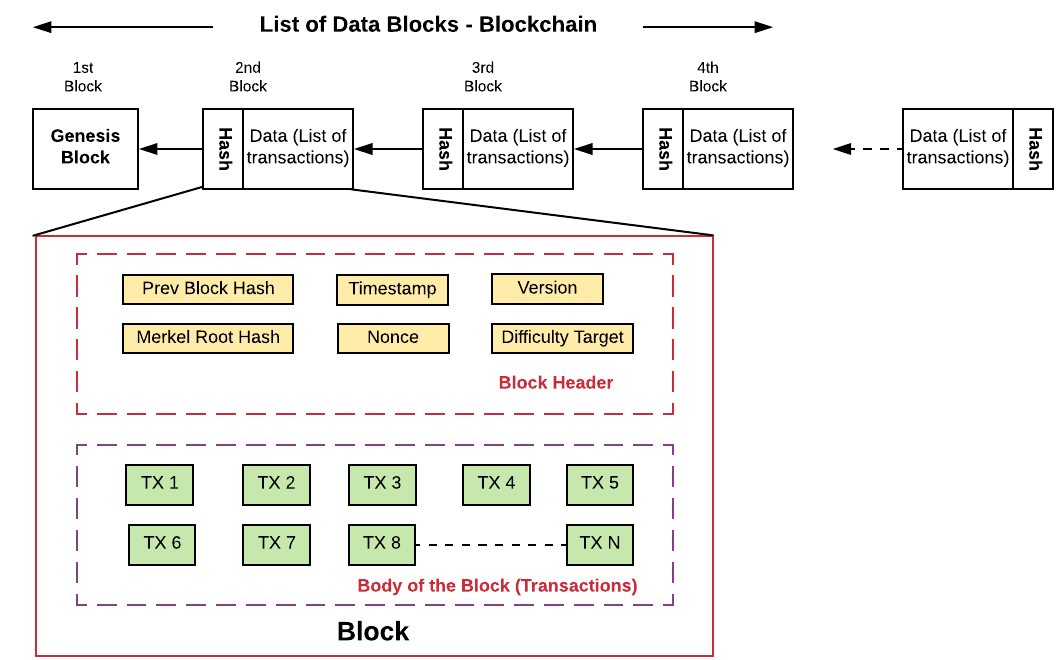



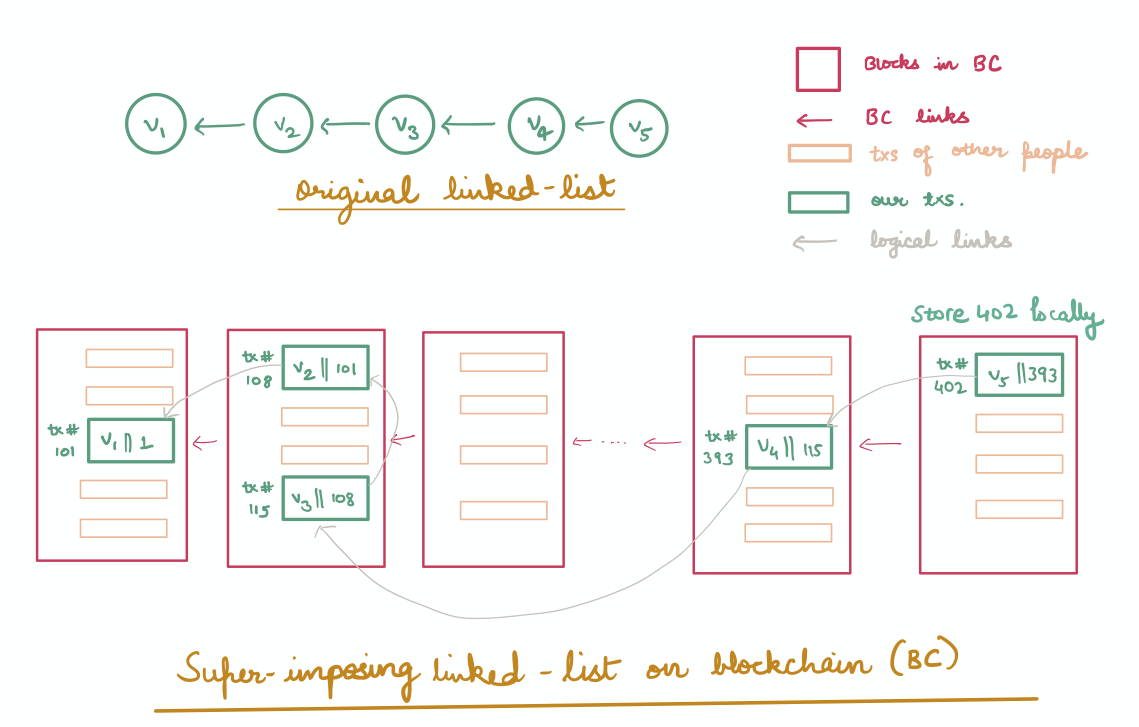
Is Blockchain A Linked List Like Data Structure Data Analytics



Blockchain Data Structure Download Scientific Diagram



Details Oracle Blockchain Table



In Blockchain If Data Is Hashed And Stored And Hashing Is A One Way Function How Can We Retrieve The Actual Data From Blockchain Quora




Building A Blockchain Database With Mongodb




Health Care Blockchain And Innovative Uses Freed Associates




Blockchain Vs Distributed Ledger Technology A Detailed Guide



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿